

Medically reviewed by Dr. Sim Hsien Lin, Consultant General Surgeon (Colorectal Surgery)
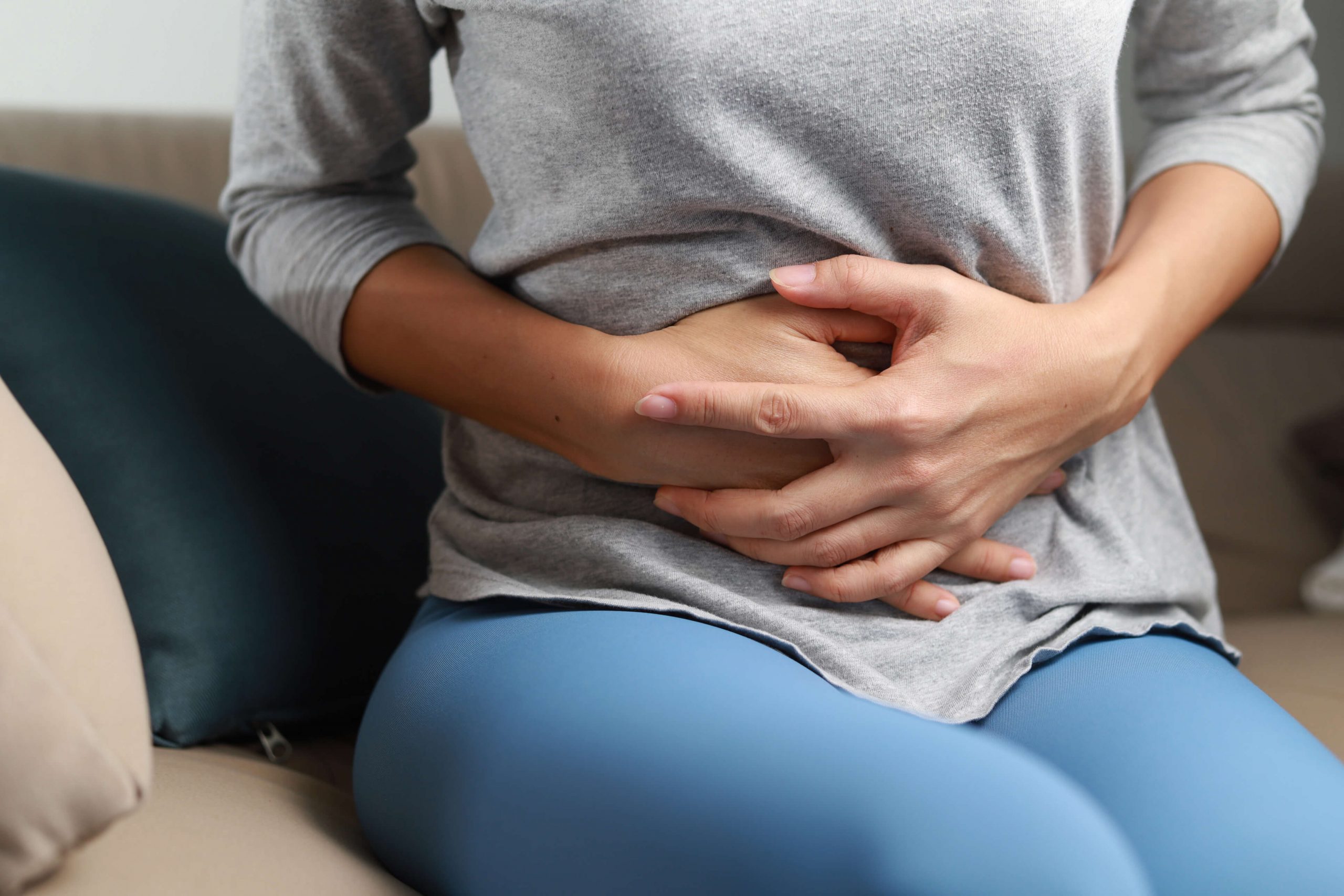

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal or bowel disorder featuring recurrent abdominal pain with diarrhoea or constipation. IBS is mainly a disorder of gut motility and function. For people diagnosed with IBS, gut movements are sometimes faster and, at other times, slower. The symptoms of IBS varies, some people have diarrhoea as a predominant symptom, while others have constipation as a predominant symptom. There can be cases of IBS with both diarrhoea and constipation symptoms alternatively.
IBS is a fairly common condition, with prevalence rates of 10-15% worldwide. It has been found that IBS is more common in women than in men. IBS can occur at almost any age, but it typically affects adults of age group 30 to 40 years old.
It’s worth noting that IBS is a different condition from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. IBS is not a life-threatening condition nor does it produce any serious complications. It does not increase your risk for colon cancer, nor does it cause any structural damage or changes in the colon. Nevertheless, IBS can be distressing and may have a great impact on work and daily life.
The underlying cause of IBS is not known clearly. However, multiple factors appear to play a role in causing IBS and act as triggers for the IBS symptoms. Below are some of the well-known triggers or risk factors for IBS.
Symptoms tend to come in phases or episodes that can last for days to weeks and may relapse after a certain time. Symptom intensity ranges from mild to severe and differs between individuals, for severe cases, it can even affect their daily lives. The most frequently reported symptom is abdominal pain. Abdominal pain can be localized or generalized, which is instantly relieved with the passing of stool or gas. The stool is not too watery but most often, mucus is present. People who have IBS, generally report to the doctor with the following symptoms:
IBS is diagnosed based on your clinical history, past medical history and with no clinical evidence of other gastrointestinal diseases. It’s worth noting that IBS is diagnosed only if your symptoms are present for more than six months and do not have any other similar conditions. No visible changes are noted on abdominal X-ray, endoscopy or colonoscopy if you have IBS.
Based on clinical features, you might need to undergo some tests for further evaluation and diagnosis: Blood tests, Urinalysis and urine culture, Stool culture, Faecal occult blood test, Abdominal X-ray, Abdominal Ultrasound, Colonoscopy. If test results are normal and not pointing towards other conditions, it is more likely you have IBS.
It must be understood that several other conditions do present with similar symptoms. So it is important to elicit a detailed clinical history and rule out other diagnoses. If a person presents with rectal bleeding, significant weight loss or fever along with symptoms of IBS, it can indicate other diseases and should seek medical advice.
Following are the differential diagnosis of IBS:
There is no known cure for IBS, but it is possible to manage the symptoms through multiple approaches.
If you have IBS, you might need to be cautious about certain foods you consume in your diet, as certain foods can be the triggers for IBS symptoms. You will also need to follow diet habits.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a fairly common digestive disorder that can cause repeated abdominal pain and changes in bowel movements. The symptoms occur intermittently and can be a lifelong problem. IBS can significantly impact your daily life leading to frustration, anxiety, and depression. Since many conditions can mimic the symptoms of IBS it is important to seek help from a healthcare provider. There is no definitive cure for the disorder but your doctor may help find the treatment that works best for you. Dietary modification, probiotics, and medications can improve symptoms and the quality of life. Leading an active and healthy lifestyle is also beneficial.



Dr. Sim Hsien Lin is a specialist colorectal surgeon in Singapore with over 10 years of experience in colorectal surgery. Her sub interests include laparoscopic colorectal surgery, transanal endoscopic microsurgery (TEMS), surgical management of piles, inflammatory bowel diseases and complex anal fistulas.
Read Full BioCome visit our clinic, which are equipped with modern and updated equipment, and a team that will take care of all your needs.
Dr. Sim became a Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons (Edinburgh) in 2011, winning the Gold Medal award at the FRCS Exit Examination that year.
Dr. Sim firmly believes that transdisciplinary care is the key to supporting both the elderly and complex patients through their perioperative and recovery journey.
Dr. Sim firmly believes that transdisciplinary care is the key to supporting both the elderly and complex patients through their perioperative and recovery journey.
Book An AppointmentPlease fill up this form and we’ll get back to you shortly!

For quicker response, call us at+65 6261 9227

Chat with our friendly clinic staff through WhatsApp!